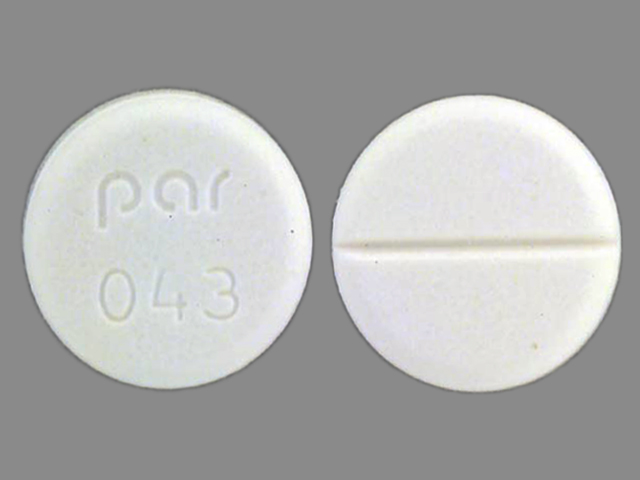
What is Cyproheptadine?
Cyproheptadine is an antihistamine that decreases the effects of the natural chemical histamine within the body. Histamine is known to cause nasal congestion, itching, eye watering, and nasal congestion.
Cyproheptadine can treat nasal sneezing, runny nose itching, dry or red eyes, and other signs that are a result of allergies during the season (hay fever). Cyproheptadine can also be used to treat other conditions, like eczema, as well as skin reactions due to bites from insects. Cyproheptadine may be used to treat certain kinds of headaches, such as migraines. Cyproheptadine is also used for reasons not mentioned in this guideline for medication.
Side effects of Cyproheptadine
Contact a medical professional immediately. If you are experiencing symptoms that indicate an allergic reaction, such as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of your lips, face, or tongue,
Cyproheptadine can cause serious adverse side effects. Stop taking cyproheptadine immediately and contact your physician immediately. If you suffer from:
- A lightheaded sensation, similar to what you're passing out;
- Tremor, seizure (convulsions);
- Confusion, hallucinations;
- Minimal or no urination
- Rapid heartbeats or fast beats;
- Bleeding or bruising;
- Your ears are ringing, or
- Yellowed, pale skin. Dark-colored blood, fever, and weakness
Common adverse effects of cyproheptadine could include:
- Drowsiness, dizziness;
- Dry mouth, nose, dry mouth, or throat;
- Constipation;
- Blurred vision or
- Being anxious or restless (especially for children).
This is not a comprehensive list of possible side effects, and others could happen. Consult your physician for advice regarding medical adverse effects. You may report any adverse reactions to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Similar/related drugs
Ubrelvy, Botox, Prednisone, Hydroxyzine, Diclofenac, Fluticasone Nasal, and Loratadine
Warnings
It is not recommended to use cyproheptadine when you suffer from narrow-angle glaucoma, a stomach ulcer or obstruction, increased prostate or urination issues, or if you're experiencing the symptoms of an asthma attack. It is also not recommended to use cyproheptadine while breastfeeding infants who are over the age of 65 or have an illness that is debilitating.
Do not take cyproheptadine in the event that you've used an MAO inhibitor within the last 14 days, including isocarboxazid linezolid blue injections, phenelzine rasagiline, or selegiline.
Antihistamines should not be used as medications to make children tired.
Prior to use this drug
It is not recommended to use cyproheptadine if you have an allergy to it or
- You have glaucoma with a narrow angle.
- If you suffer from stomach ulcers or obstruction
- If you suffer from an overly large prostate or have problems with urination,
- You are breastfeeding the baby.
- You're suffering from an asthma attack.
- If you're over the age of 65 or have an illness that is debilitating,
Don't give this medication to a premature or newborn child. Cyproheptadine is not permitted for use by any person who is less than two years old.
To ensure that cyproheptadine is appropriate for you, consult your doctor if:
- Glaucoma;
- An asthmatic history;
- High blood pressure;
- Heart disease or
- An overactive thyroid.
Cyproheptadine isn't expected to cause harm to an unborn child. Inform your doctor if you are expecting or planning for pregnancy while taking this medication.
It is unclear if cyproheptadine is absorbed into breast milk or if it harms the nursing infant. Antihistamines may slow breast milk production. Do not breastfeed when taking this medication.
How to take Cyproheptadine?
Follow the instructions on the prescription label. Your doctor could change your dosage to ensure you are getting the best outcomes. Avoid using cyproheptadine in greater or lesser quantities or for longer periods than suggested. Don't give this medicine to children younger than two years old. It is not recommended to apply antihistamines to make your child sleepy. Death can occur because of the use of antihistamines in young children. Measure the amount of liquid medicine using the dosing syringe that comes with it, or use a measuring spoon or cup for measuring doses. If you don't own a device for measuring doses, request one from your pharmacist. one.
Consult your physician. If you experience any weight changes, Cyproheptadine dosages are based on weight (especially in teenagers and children), and any changes could affect the dosage. This medication can cause an untrue positive test for drugs. If you give the urine sample to conduct drug screening, notify the laboratory personnel that you're taking Cyproheptadine. Place in a tightly sealed container that is kept at room temperature, far from heat and moisture.
What happens if I miss the dose?
Do the missed dose as quickly as you can remember. Do not take your missed dose if it's nearing the time for the next dose. Don't take any extra medication to make up for the missed dose.
What happens if I overdose?
For medical emergencies, seek emergency medical attention or contact the Poison Help Line toll-free at 1-800-222-1222.
Overdose symptoms can include severe hallucinations, extreme dry mouth, pupils that are dilated and skin that is pale or reddish, tingling, vomiting, anxiety (in children), weak or shallow breathing, or seizures (convulsions).
What should be avoided?
Cyproheptadine could affect your ability to think or react. Be aware when you drive or perform things that require you to remain vigilant.
Alcohol consumption with this medicine may cause unwanted side effects.
Interaction with other drugs
If you are taking cyproheptadine along with other medicines that cause sleepiness, it could make you more sleepy. Consult your physician before taking a narcotic, sleeping pill, medication, muscle relaxer, or medication to treat anxiety, depression, or seizures.
Other medications may interfere with cyproheptadine. This includes prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Inform your health professionals about the medicines you are taking in the present and about any medication that you decide to stop or change your use of.