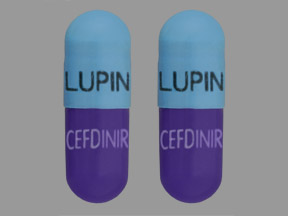
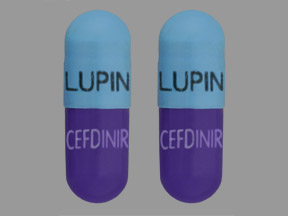
What is Cefdinir?
Cefdinir is a bactericidal (SEF is a low-spore) antibiotic that is utilized to treat various types of infections due to bacteria.
Cefdinir can also be utilized for other purposes that are not mentioned in this guideline.
Side effects of Cefdinir
Contact emergency medical assistance. If you notice symptoms that indicate an allergic reaction (hives, breathing problems, and swelling on your throat or face) or you experience a serious skin reaction (fever, sore throats, burning eyes, facial discomfort, purple or red skin with blisters as well as peeling),
Cefdinir may cause serious side effects. Consult your physician right away if you experience:
- Extreme stomach pains; diarrhea that appears bloody or watery (even when it happens some time after the most recent dosage);
- Fever, chills, body aches, flu symptoms;
- Pale skin, easy bleeding, unusual
- Seizure (convulsions);
- Fever, weakness, and confusion;
- Urine that is dark-colored, jaundice (yellowing of eyes or skin), as well as
- Kidney issues: little or no urine output; swelling of your ankles or feet; fatigue or tiredness.
A common adverse effect associated with cefdinir can comprise:
- Nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea;
- Vaginal irritation or discharge
- Migraine,
- Rashes (including diaper rash) when a baby is using liquid cefdinir
This is not an exhaustive listing of all side effects. There are other possible side effects. Consult your physician for advice regarding medical adverse effects. It is possible to report any side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Warnings
Don't take cefdinir. If you're allergic to cefdinir or the same antibiotics that include ceftin, cefzil, and Keflex, as well as others.
Before you Take this Drug
It is not recommended to take this drug if you are intolerant to cefdinir or other antibiotics made of cephalosporin (cefadroxil, cefprozil, cefazolin, Cefalexin, Keflex, and others).
Inform your physician if you were ever diagnosed with:
- Kidney disease (or the condition if you're currently on dialysis);
- Issues with the digestive tract, for example, colitis, as well as
- An allergy to all drugs (especially penicillins).
Cefdinir liquid contains sucrose. Discuss with your doctor prior to taking this type of cefdinir if you suffer from an illness like diabetes.Consult your doctor if you are breastfeeding or pregnant.
How to Take Cefdinir?
Be sure to follow all the directions printed on your prescription label and review all the medication guides or instructions. Make sure you use the medicine according to the directions.
Make sure to shake off your oral suspension (liquid) prior to using it to determine a dose. Utilize the syringe for dosing as well as a dosage-measuring device (not an ordinary spoon).It is possible to take cefdinir either in combination with or without eating.
Utilize cefdinir for the entire duration of the prescription, regardless of whether your symptoms do not improve immediately. Inadequate doses could increase the chance of developing an illness that is intolerant to medications. Cefdinir does not cure the symptoms of a viral disease, for example, influenza or a commonly occurring cold.Cefdinir could affect the outcome of medical tests. Be sure to inform any doctor treating patients that you're taking cefdinir.
Place it in a cool, dry place free of heat and moisture. Discard any cefdinir liquid that has been stored for more than 10 days.
Details on Dosage
Usual Adult Dose for Pneumonia:
The community was given 300 mg of oral medication every 12 hours over a period of 10 to 14 days.
Usual Adult Dose for Bronchitis:
In acute exacerbations caused by chronic bronchitis In the event of acute exacerbations, 300 mg is taken orally per 12 hours over five to 10 days, or 600 mg is taken orally throughout the day for 10 days.
Usual Adult Dose for Sinusitis:
Maxillary sinusitis The dosage is 300 mg per day orally (or 600 mg daily) for 24 hours over 10 days.
Usual Adult Dose for Skin or Soft Tissue Infection:
Simple: 300 mg taken orally every 12 hours over 10 days.
Usual Adult Dose for Tonsillitis or Pharyngitis:
300 mg of oral medication every 12 hours for 5–10 days, or 600 mg orally every 24-hours for 10 consecutive days.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Pneumonia:
Community purchased:
13 or over at least 12 hours from 10 to 14 days
Usual Pediatric Dose for Bronchitis:
The acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis
13 or over Age 13 or over: 300 mg taken orally every 12 hours during 5 to 10 days or 600 mg taken orally each 24 hours for 10 consecutive days
Usual Pediatric Dose for Otitis Media:
An acute infection with the bacterium Otitis media
From 6 months to 12 years old: 7 mg/kg taken orally daily for five to 10 days or 14 mg/kg orally every day for 10 consecutive days
Maximum dose: 600 mg/day
Usual Pediatric Dose for Tonsillitis or Pharyngitis:
From 6 months to 12 years old: 7 mg/kg oral each 12 hours over five to 10 days or 14 mg/kg daily orally for 24 hours for a period of 10 days
Maximum dose: 600 mg/day
Age 13 and over: 13 years or older: 300 mg daily for 12 hours during 5 to 10 days, or 600 mg oral throughout the day for 10 consecutive days
Usual Pediatric Dose for Sinusitis:
Sinusitis, acute and chronic:
Six months through 12 years of age: 7 mg/kg taken orally in 12 hours, or 14 mg/kg throughout the day for 10 consecutive days
Maximum dose: 600 mg/day
Age 13 or over Age 13 or over: 300 mg taken orally every 12 hours, or 600 mg daily orally for all day, for a total of 10 days.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Skin and Structure Infection:
Uncomplicated:
6-months to 12 years of age: 7 mg/kg oral throughout the day for 10 consecutive days
Maximum dose: 600 mg/day
Age 13 and over: at least 12 hours for a period of 10 days
What Happens If I Miss a Dose?
You should take your medicine as quickly as you are able, but avoid the dose you missed when it's almost time to take the next dose. Take two doses simultaneously.
What Happens If I Overdose?
For medical emergencies, seek emergency treatment or dial for help at the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
Overdose symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea, or a seizure.
What Should be Avoided?
Beware of using analytic drugs or supplements with minerals such as magnesium, iron, or aluminum within two hours prior to or immediately after taking cefdinir. Iron or antacids can make it a problem for the body to absorb cefdinir. This doesn't include infant formula that is enriched with iron.
The use of antibiotics can trigger diarrhea, which could indicate an infection that has just started. If you are experiencing diarrhea that's watery or bloody, consult your physician prior to taking antibiotics to treat diarrhea.
Interaction with Other Drugs
Inform your physician about any other medications you take, particularly:
- Probenecid;
- Vitamin or mineral supplements containing iron
This is not a complete list. Certain other drugs can interact with cefdinir's effects, such as prescription or OTC medicines, vitamins, and herbs. There are many possible interactions between drugs. are included here.