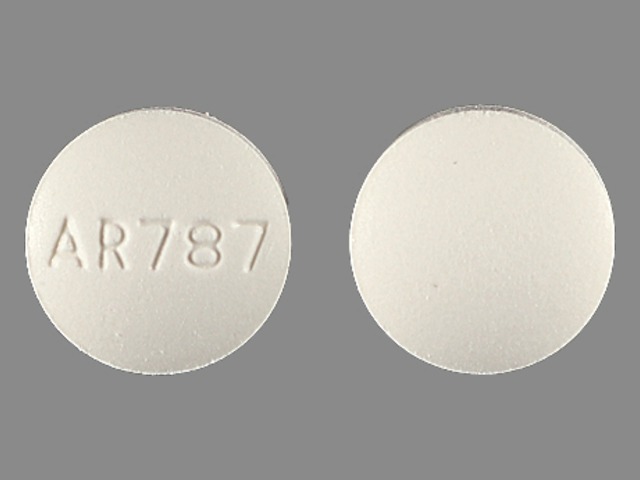
What is Fenofibric acid?
Fenofibric acids help reduce cholesterol levels and also the triglycerides (fatty acids) in the blood. The presence of high levels of these kinds of fats in the blood can lead to an increase in the risk of atherosclerosis (clogged arterial blood vessels). Fenofibric acid is often prescribed along with other medications for lowering cholesterol. Fenofibric acid can be used to treat other conditions that are not mentioned in this guideline.
Side effects of Fenofibric acid
Contact emergency medical assistance if you experience symptoms that indicate an allergic response (hives and breathing problems, swelling in your throat or face) or severe skin reactions (fever and eye burns, skin irritation leading to red or purple patches that blister and peel), which could require emergency assistance.
In rare instances, fenofibric acid may cause a condition that leads to the destruction of skeletal muscle tissue, which can lead to renal failure. Consult your doctor immediately in the event of unexplained muscle discomfort, tenderness, pain, or weakness, especially if you suffer from unusual fatigue, fever, or a dark urine color.
Contact your doctor at anytime if you suffer from:
- Sharp stomach pain that spreads into your shoulder or back blade
- Inability to eat and stomach pains after a meal
- Jaundice (yellowing of the eyes or skin);
- The symptoms include chills, fever, weakness, sore throatweaknessulcers, unusual bleeding or bruising;
- Chest pain, a sudden cough, wheezing, and rapid breathing. You may also cough up blood or
- Swelling or warmth in the leg or arm.
Common adverse effects of fenofibric acids could include:
- Nose that is runny, sneezing, or
- Laboratory tests that are abnormal
This isn't a complete list of possible side effects, and other effects may also be present. Contact your physician to seek medical advice on the effects. You can report any side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Warnings
Fenofibric acid is not a good acid if you suffer from a liver condition, gallbladder disease, or extreme kidney disease and are breastfeeding a child.
Fenofibric acids can trigger the destruction of muscle tissue. This could result in kidney failure. Contact your physician immediately in the event of unprovoked muscle tenderness, pain, or weakness, especially in the event that you are also suffering from fatigue, an unusually high fever, or dark urine.
Before you take this drug
It is not recommended to take this medicine if you are sensitive to fenofibric acids or fenofibrate or are:
- Severely kidney-related disease (or if you're taking dialysis);
- Liver disease liver disease
- Gallbladder disease.
Avoid breastfeeding during the course of this medication and for a minimum of 5 days following your last dose.
Speak to your doctor if you have ever suffered from:
- Kidney disease;
- Liver disease liver disease
- Gallbladder issues.
Fenofibric acids can trigger the destruction of muscles, which can cause kidney failure. This is more common in people who are older as well as those suffering from renal disease, the condition known as diabetes, or hypothyroidism that is not properly controlled (underactive thyroid).
It isn't known if this medication could affect a newborn baby. Consult your physician if you are pregnant or planning to be pregnant. Fenofibric acid is not a drug allowed for use by any person who is younger than
How to take Fenofibric acid?
Follow the directions on your prescription label, and review all medication guides and instructions sheets. The doctor might alter the dosage. Make sure you take the medication exactly as prescribed.
You can take fenofibric acids in combination with or without meals. Take the capsule or tablet in its entirety and don't break, crush, dissolve, or even open it. It is possible that you require regular medical tests. Even if you don't have symptoms, tests can aid your doctor in determining the effectiveness of fenofibric acid. Fenofibric acids are only a part of a full program of treatment that could also encompass diet, exercise, weight loss, and other medicines. Make sure you follow your diet, medications, and exercise routines with the utmost care. Place it in a cool, dry place far from heat and moisture.
Details on dosage
Usual adult dose for hypertriglyceridemia:
Capsules:
Initial dose: 45–135 mg taken orally, once a day.
Maximum dose: 135 mg once a day.
Tablets:
Initial dosage: 35–105 mg taken orally daily.
Maximum dose: 105 mg once a day.
Comments:
Dosages must be adjusted in accordance with the patient's response and, when necessary, adjusted after regular lipid measurements between 4 and 8-week intervals.
Improving the control of glucose in patients with diabetes who have fasting chylomicronemia can usually eliminate the need for intervention with pharmacologic drugs.
Triglycerides with elevated (TG) levels at or above 2000 mg/dL could increase the chance of developing pancreatitis. The effect of treatment to reduce this risk has not been fully investigated.
Uses:
as an aid to diet, to decrease TG in patients suffering from severely hypertriglyceridemia (500 mg/dL or more).
Usual Adult Dose for Hyperlipidemia:
Capsules:
135 mg orally, twice per day.
Tablets:
100 mg orally, at least once per day.
Use: As an add-on to a diet plan to lower elevated lower-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and total cholesterol (Total-C), as well as TG and apolipoprotein A (Apo B), as well as to increase the amount of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in patients suffering from chronic hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia.
Usual Adult Dose for Dyslipidemia:
Capsules:
135 mg orally, twice per day.
Tablets:
Orally, 105 mg every day, once
Use: As an add-on to a healthy diet to lower low-density cholesterol (LDL-C) and total cholesterol (Total-C), TG, and apolipoprotein A (Apo B), and to boost high-density cholesterol (HDL-C) in patients suffering from primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia.
What happens if I miss a dose?
You should take the medication as quickly as you can. However, do not take any missed doses if you are close to the time of the next dose. Don't take two doses at a time.
What happens if I overdose?
Get medical attention in an emergency or contact the Poison Help Line toll-free at 1-800-222-1222.
What should be avoided?
Do not eat foods with high levels of cholesterol or fat; fenofibric acids will not work as well.
Do not drink alcohol. It may raise the levels of triglycerides and increase the risk of damage to your liver.
Interaction with other drugs
Certain medicines may cause fenofibric acids to be less effective if taken simultaneously. If you are taking any of these medicines, you should take your fenofibric acid dose an hour before or for 4 to 6 hours after having taken the other medication.
- Cholestyramine;
- Colesevelam; or
- Colestipol.
Discuss with your doctor any other medications you take, including:
- Other medicines to lower cholesterol include
- Colchicine;
- A blood thinner, such as warfarin, coumadin, jantoven, or
- Medications that reduce the strength of your immune system, such as cancer medicines, steroids, and other medications that hinder organ donation
This list isn't exhaustive. Other drugs can interact with fenofibric acid, such as medications that are prescribed and available over the counter, vitamins, and herbal supplements. There are many possible interactions between drugs that are listed here.