Autoimmune diseases can sound pretty intimidating, can’t they? Going to the doctor is like having your own immune system attack your body. Instead of shield you from foreign bodies such as virus and bacteria, it begins to destroy the healthy cells in your body. Crazy, but true. Over 80 autoimmune diseases are recognized today, and while they differ in the areas they target, they all share a similar culprit: The immune system itself becoming out of control.
In this post, however, we will discuss some of the most prevalent autoimmune diseases, signs and therapies that are available to assist individuals who have these diseases.
What are the Autoimmune Diseases?
Autoimmune diseases are diseases where the body produces an immune response against its own tissues or cells. This firing can cause a constant inflammation, tissue injury and a lot more pain. But why does this happen?
-
Genetics: If you are born with a certain genetic makeup, your chances of developing the disease increase. If one of your family members has autoimmune disease, it means that you are at a higher risk of developing autoimmune disease yourself.
-
Environment: Some infections, toxins or even exposure to sunlight can cause the immune system to become sensitive.
-
Lifestyle factors: It may also be due to diet, stress, and lack of sleep to mention but a few.
Consequently, approximately 50 million Americans have autoimmune diseases based on the information provided by the American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association (AARDA). In diagnosing them, it is difficult because the signs and signals are not always the same and even if treated, there is no actual cure for the diseases.
Most Common Autoimmune Diseases and Their Treatments
1. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
RA is a sneaky one. It mostly targets the joints, causing swelling, stiffness, and pain. Over time, it can damage cartilage and bones, leading to deformity. The immune system attacks the synovium, a tissue lining the joints, which results in inflammation.
Treatment for RA:
-
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): These reduce pain and swelling.
-
DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs): Medications like methotrexate slow down RA’s progress by calming the immune system.
-
Biologic Agents: A special class of DMARDs that target specific parts of the immune system to block inflammation.
-
Physical Therapy: Helps improve mobility and flexibility, making daily life a little easier for RA sufferers.
Did you know? Nearly 1.5 million Americans are living with RA, with women being two to three times more likely to develop it than men.
2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Lupus is one of the more complex autoimmune diseases because it can affect multiple organs, including the skin, kidneys, heart, and lungs. The immune system creates antibodies that attack healthy tissues, causing widespread inflammation.
Treatment for SLE:
-
NSAIDs: These are used to reduce inflammation and manage pain.
-
Corticosteroids: Powerful drugs to control severe flare-ups and inflammation.
-
Antimalarials: Drugs like hydroxychloroquine are often prescribed to manage lupus symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
-
Immunosuppressive Agents: These medications, like azathioprine, help to tone down the immune response.
A surprising fact: 90% of lupus patients are women, with symptoms often showing up between the ages of 15 and 44.
3. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
MS targets the central nervous system. The immune system attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, known as myelin, leading to nerve damage. Symptoms include muscle weakness, numbness, and coordination issues, which can progressively worsen over time.
Treatment for MS:
-
Disease-Modifying Therapies (DMTs): These drugs slow the progression and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
-
Corticosteroids: Used to reduce inflammation during relapses.
-
Physical, Occupational, and Speech Therapies: To help maintain mobility, strength, and speech functions.
MS affects around 1 million people in the U.S., with more than twice as many women diagnosed as men.
4. Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to dangerously high blood sugar levels. Without insulin, the body can’t properly use glucose for energy.
Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes:
-
Insulin Therapy: Since the pancreas can’t produce insulin, patients must rely on insulin injections or pumps.
-
Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regular checks help people adjust insulin doses and maintain healthy levels.
-
Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet and regular exercise play key roles in managing blood sugar.
Approximately 1.6 million Americans have type 1 diabetes, including about 200,000 children and adolescents.
5. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
This disease impacts the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid). It’s caused by the immune system attacking the thyroid, which disrupts hormone production and leads to fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance.
Treatment for Hashimoto’s:
-
Thyroid Hormone Therapy: Daily doses of synthetic thyroid hormones help regulate metabolism.
-
Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet and regular exercise can also help manage symptoms.
Hashimoto’s affects about 5 in 100 Americans, and women are about 8 times more likely to develop it than men.
6. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
IBD includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, both of which cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss can significantly impact daily life.
Treatment for IBD:
-
Anti-inflammatory Drugs: These help reduce inflammation in the gut.
-
Immunosuppressive Agents: Medications like azathioprine and methotrexate control the immune response.
-
Biologics: Drugs like infliximab target specific inflammatory molecules.
Around 1.6 million Americans live with IBD, and cases are on the rise.
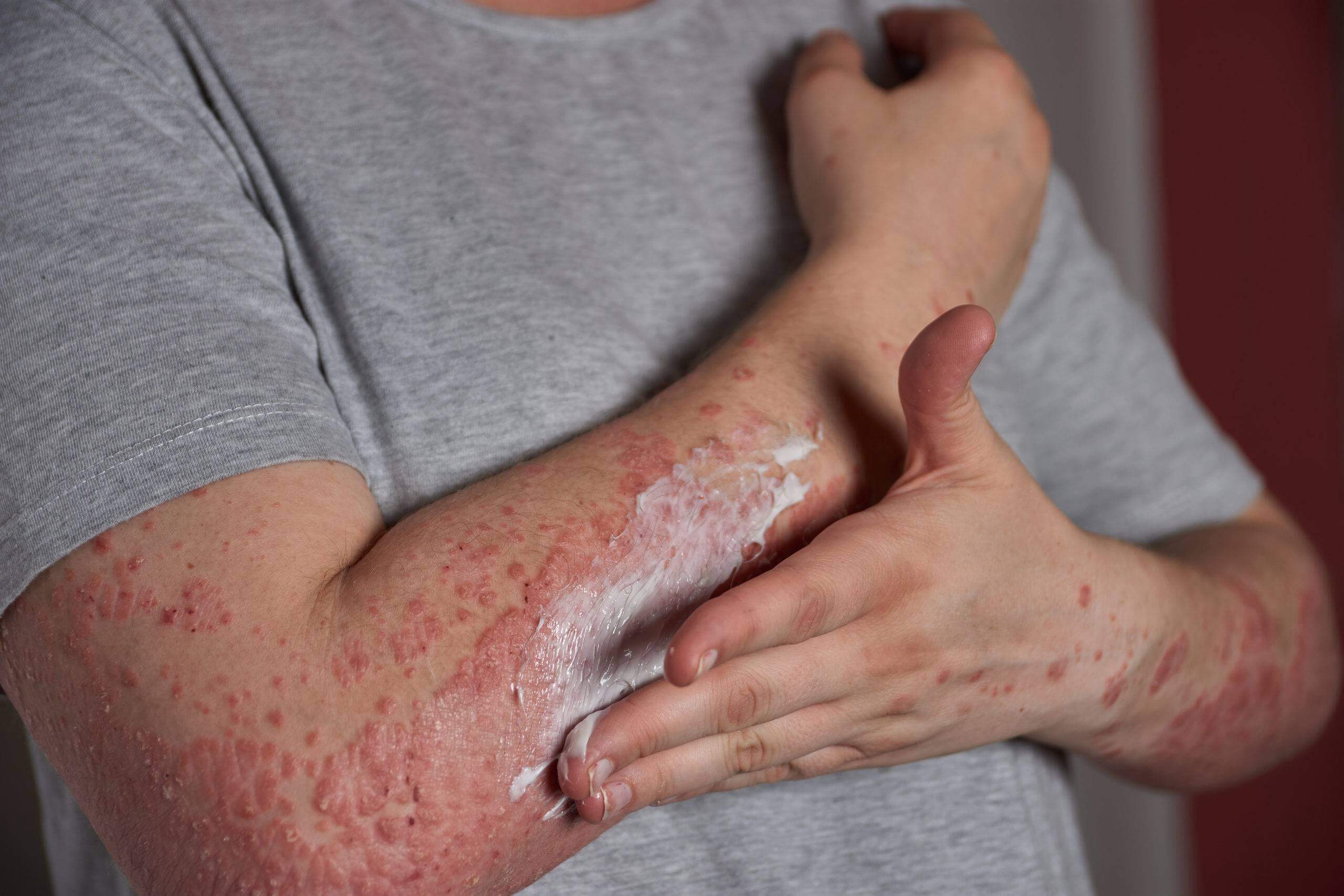
7. Psoriasis
This skin condition causes red, scaly patches that can be itchy and painful. The immune system triggers an overproduction of skin cells, leading to the characteristic scaling.
Treatment for Psoriasis:
-
Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments that reduce inflammation and slow down skin cell production.
-
Phototherapy: Exposure to controlled UV light helps reduce inflammation.
-
Systemic Medications: These include biologics and other drugs that suppress the immune system.
Psoriasis affects about 7.5 million people in the U.S., and it’s not just a skin problem—it can also affect the joints, leading to psoriatic arthritis.
8. Sjogren’s Syndrome
Sjogren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disease that mostly affects the glands that secrete saliva and tear, resulting in dry mouth and dry eye.
Treatment for Sjogren’s:
-
Artificial Tears and Saliva Substitutes: These assists to reduce dryness and itching.
-
Immunosuppressive Agents: These medications help to decrease inflammation and output of the body’s defense mechanisms.
-
Lifestyle Changes: They should also avoid caffeine and ensure that they take a lot of fluids in order to minimize such symptoms.
Sjogren’s affects approximately 4 million people in the United States, majority of whom are women above 40 years of age.
Habits to Follow For Autoimmune Diseases
While medications play a crucial role, they are not the only solution. You can also make significant strides in managing your autoimmune disease by adopting lifestyle changes. Here are some helpful tips:
-
Stay Active: Exercise also helps lower inflammation levels and enhanced joint and muscle functionality.
-
Healthy Diet: To reduce inflammation, individuals should take foods that have high amount of omega-3 fatty acids such as fish.
-
Stress Management: There are certain activities that should be avoided, or at least done advisedly: stress is a major factor in a flare-up, and stress reduction techniques such as yoga or meditation should be employed.
-
Sleep Well: Rest is essential in the body to help it conquer stress and also is important for the body to be able to get enough rest.
Last Words
Autoimmune diseases can be tough to live with, but with proper treatment and care, many people lead full, active lives. Working closely with healthcare providers, keeping an eye on symptoms, and making lifestyle changes can make managing these conditions much easier. It is always better to be informed and make sure you consult your doctor for the best choices for you.