Pathogens cause skin infections including bacteria and viruses. The symptoms, treatment outlook depend on the situation whether it is mild to serious. We can treat most skin infections. Infection can become more serious when it penetrates deeper into the skin. People with a weakened immune system get more chances of skin infections. This could be due to HIV, diabetes or malnutrition. People get some side effects of medication, such as chemotherapy.
Read on to learn more about skin infections and what we can do about them.
What Are Types of Skin Infection?
There are four different types of skin infections which are as follows:
1. Bacterial Skin Infections
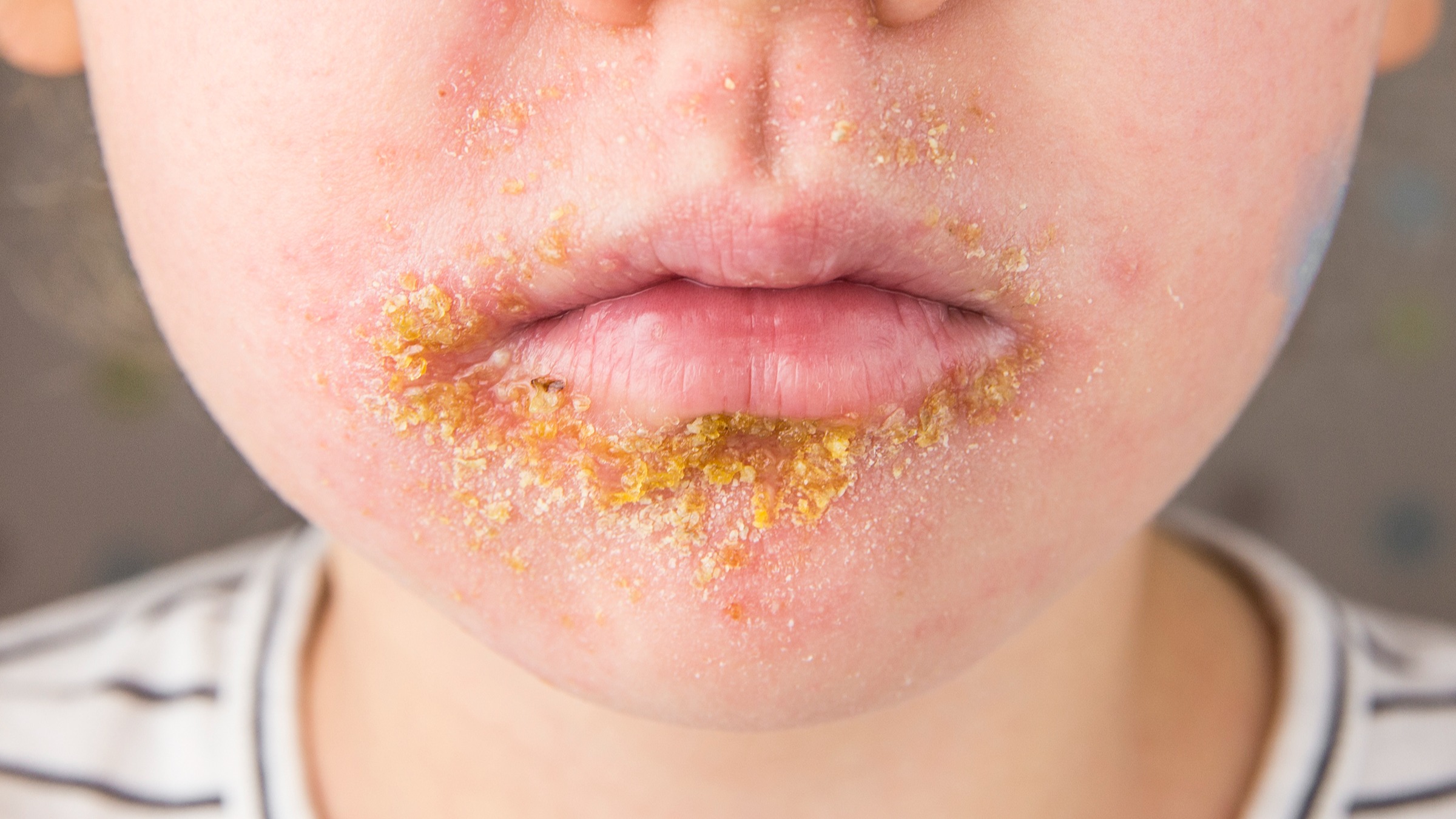
Bacterial skin infections occur when bacteria enter the skin via outdoors. They enter the skin through a hair follicle and anthrax is a bacterium that enters from the environment. Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are bacteria that are present on the skin. Bacterial infections can be systemic or local and produce symptoms like fever in the body. While local infections only affect a specific area and never spread throughout the body.
Bacterial skin infections like impetigo spread between people through direct skin contact or food that is contaminated. Others, cellulitis, we can call it non-contagious.
Types of bacterial skin infections include:
- Cellulitis
- Impetigo
- Boils
- Leprosy
Systemic infections include which causes rashes on skin:
- Syphilis
- Tuberculosis
Some bacterial infections are easy to treat with antibiotics, but others require an antibiotic along with proper medical treatment.
2. Viral skin infections
Viruses cause skin symptoms, such as:
- shingles
- chickenpox
- measles
- Rashes on hand, foot, and mouth
These viruses are contagious, and systemic.
3. Fungal skin infections
These types of skin infections are caused by a fungus in moist areas of the body, such as the feet and armpit.
In other cases, an allergy to the fungus causes a fungal infection on the foot. It also develops a rash on their fingers.
Different types of fungal infections:
- athlete’s foot
- yeast infection
- ringworm
- nail fungus
4. Parasitic skin infection
Skin infections are caused by a parasite and spread beyond the skin to the bloodstream. A parasitic infection isn’t life-threatening. Parasitic skin infections include:
- lice
- bedbugs
- scabies
What are the symptoms of a skin infection?
Symptoms may include:
- redness on skin, or purple areas of skin
- lesions that are raised and bumpy
- itching
- pain
In some cases, people may also have a fever.
Signs of a severe infection include:
- pus
- blisters
- pain and discoloration
- swelling
Bacterial skin infection
When bacteria enter the body through a cut in the skin.
Not all cuts lead to a skin infection, but a higher risk may occur:
- Weakened immune system
- Do not clean the wound
- when working outside, exposed to bacteria
Viral skin infection
Common viruses come from groups of viruses:
- poxviruses
- molluscum contagiosum
- smallpox
- Mpox
- human papillomavirus (HPV) that leads to genital warts
- herpes viruses, that causes herpes simplex viruses (HSV)
- varicella-zoster virus, which causes chickenpox
- Epstein-Barr virus which lead to mononucleosis
Fungal infection
Body lifestyle factors increase the risk of a fungal infection which grows in warm environments.
Some risk factors are:
- having sweaty feet
- wearing sweaty clothes
- bathing in water that contains contamination
A cut in the skin allows pathogens to get into the skin.
Parasitic Skin Infection
Tiny insects burrowing underneath laying eggs in your skin cause a parasitic skin infection.
They include:
- Scabies: Mites, which causes itching, a rash of small pimples on the skin surface.
- Pediculosis: Lice causes this infection. It can cause lice and nits, their eggs.
- Creeping eruption: Caused by hookworms that feel snake-like rash.
Diagnosis
Doctors identify the type of skin infection based on their appearance
They ask about symptoms
- examine any rashes and any lesions
- Collect a sample of skin cells and testing in laboratory
When to see a doctor
See a doctor if you are suffering from
- Pus blisters
- Severe inflammation
- Skin infection that gets worse
- high fever
- frequent rashes and infections
Skin infections that spread into tissues under the skin or the bloodstream in people with compromised immune systems. When that happens, it leads to sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity of infection. Some infections will go away by responding to over-the-counter creams.
If an infection is severe or contagious, a doctor may prescribe medicines which includes::
- antibiotics
- antivirals
- antifungals
The form of the medication will depend on the severity and risk of complications. A person with a severe infection needs to spend time in the clinic.
Home care and Alternative Treatments
Home care for a skin infection reduces severe symptoms with tips mainly:
- Apply cold compresses to your skin several times a day which will reduce inflammation.
- Take over-the-counter antihistamines to minimize itching symptoms.
- Use topical creams to reduce discomfort.
Outlook for a Skin Infection
The outlook will depend on the severity of the infection. Many skin infections respond well to medication including methicillin-resistant. However, it is difficult to treat Staphylococcus aureus with common antibiotics.
Prevention of Skin Infection
Ways of reducing the risk of a skin rash include:
- Bathing regularly
- drying the body with towel
- sharing personal items with other people must be avoided
- checking the skin regularly for changes to look for signs of an infection
- having the vaccinations to prevent chickenpox