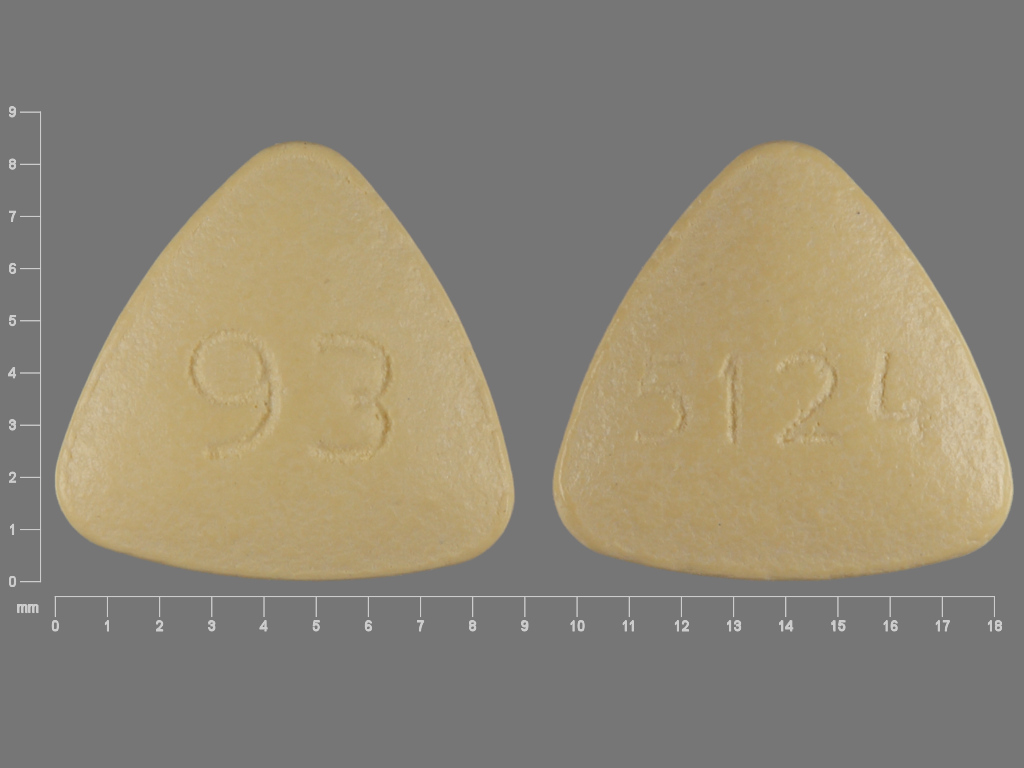
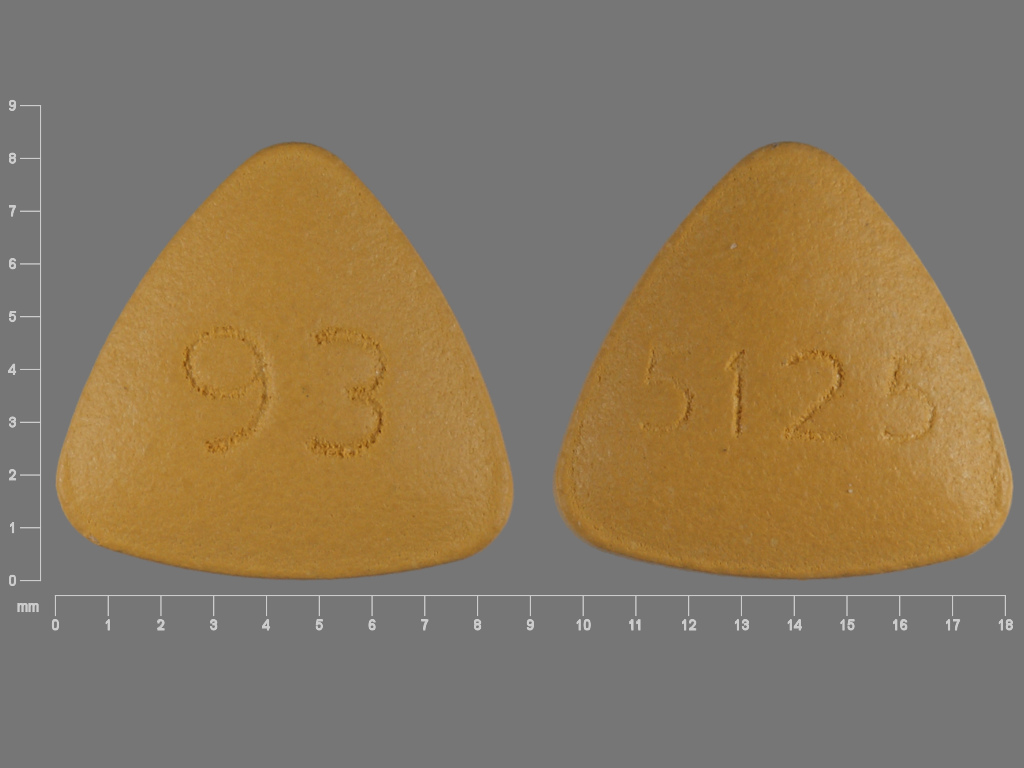
What is benazepril?
Benazepril can be used by itself or in conjunction with other medicines for the treatment of hypertension in children and adults aged 6 or older. Lowering blood pressure can reduce the risk of suffering a stroke or heart attack. Benazepril can also be used for reasons not mentioned in this medication guide.
Side effects of Benazepril
Contact a medical professional immediately. If you are experiencing warning signs of an allergic reaction such as extreme stomach pain, hives, breathing problems, swelling of your lips, face, and throat, as well as your tongue,
Benazepril may cause serious side effects:
- Feeling lightheaded, as if you're passing out.
- Kidney problems: swelling, less urination, and feeling tired or exhausted.
- High blood potassium: nausea or weakness, tingly sensation chest pain irregular heartbeats, loss of movement.
- Problems with the liver: loss of appetite nausea (upper right side) fatigue, itching, dark urine, stools that are clay-colored, and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes or skin).
Common adverse effects of benazepril could include:
- Headache.
- Cough.
This is not a comprehensive list of all the side effects. Other side effects could occur. Contact your doctor for advice regarding medical adverse effects. You can report any side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Warnings
Avoid using it when you are pregnant. Stop taking benazepril and inform your doctor as soon as possible if you find yourself pregnant. Discuss with your doctor the other medications you take. Certain medications should not be taken with benazepril.
Before you take this drug
It is not recommended to use benazepril if you have an allergy to it or the other ACE (angiotensin convert enzyme) inhibitors such as fosinopril and captopril, enalapril, lisinopril, moexipril, and perindopril. Also, there is quinapril, ramipril, or trandolapril. Take benazepril at least 36 hours after taking a medicine that has sacubitril (such as Entresto). If you suffer from diabetes, take care not to take benazepril in conjunction with any other medication that contains the ingredient aliskiren (a blood pressure medication).Be careful not to take benazepril if you've had a history of angioedema (a severe allergic reaction).
Inform your doctor if you were ever diagnosed with:
- Heart disease,like recent heart attacks.
- Stomach pain.
- Lower blood pressure.
- If you're following a diet that has low salt levels.
- Diabetes.
- Liver disease.
- Kidney disease (or those who are dialysis-dependent).
It is also possible to avoid taking benazepril in conjunction with aliskiren in the event of kidney problems. Stop taking this medication and inform your doctor immediately if you are pregnant. Benazepril can cause harm or even death to the unborn child if you use it in the third or second trimester. Do not breastfeed.
How to take benazepril?
Follow the directions on the label of your prescription and read the medication guide or instructions sheets. The doctor might alter your dosage. Follow the medication exactly as prescribed. Benazepril can be taken without or with food. Contact your physician if you are experiencing persistent diarrhea or have been sweating more than normal. You are prone to becoming dehydrated when taking benazepril. This could lead to high blood pressure levels, electrolyte imbalance, or kidney failure.
Your blood pressure needs to be monitored regularly, and you could require frequent blood tests. The treatment you receive could include exercise, diet and lifestyle modifications, and other medicines. Follow your doctor's prescriptions attentively. Inform your doctor if you are planning a procedure. Keep using benazepril even if you feel well. Close tightly in a cool, dry place far from heat and moisture.
Details on dosage
Usual Adult Dose for Hypertension:
Initial dosage: with diuretics, 5 mg taken orally once per day; without diuretics, 10 mg taken orally every day.
Maintenance dose: 20–40 mg/day, orally in one dose or in two doses equally divided.
Maximum dose: 80 mg/day
Comments: The split doses were more successful at managing pre-dosing blood pressure.
If you have stopped taking a diuretic prior to the initiation of this medication, to decrease the chance of developing hypotension, discontinue diuretic therapy within 2 to 3 days before starting this medication.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Hypertension:
6 years or older
Initial dosage: 0.2 mg/kg orally once per day as monotherapy.
Maximum dose: 0.6 mg/kg; 40 mg/day
Comments: Doses of 0.1 to 0.6 mg/kg daily have been investigated; doses that exceed 0.1 mg/kg have been shown to reduce blood pressure. Doses higher than 0.6 mg/kg (or 40 mg/day), however, have not been examined in children.
Prepare a suspension for children and patients who are unable to swallow tablets or for whom the dosage calculated is not in line with the strengths of the tablets available.
What happens if I miss a dose?
Take the medication as quickly as you can. However, avoid any missed dose if it's nearing the time to take the next dose. Never take two doses at the same time.
What happens if I overdose?
Get medical attention in an emergency or contact the Poison Help line toll-free at 1-800-222-1222.
What should be avoided?
Do not get up too quickly from a lying or sitting position, as you could get dizzy. Don't consume potassium supplements or salt substitutes unless your doctor has instructed you to.
Beware of becoming dehydrated or overheated when you exercise, during the heat, or by having a deficiency in fluids. Follow your doctor's advice on the kind and quantity of fluids you need to consume. In certain situations, drinking too much liquid could be as dangerous as drinking too little.
Interaction with other drugs
Benazepril could affect your kidneys, particularly in conjunction with other medications for infection, cancer, or osteoporosis.
Discuss with your doctor all other medicines you take, particularly:
- Diuretic, also known as a "water pill," that may boost blood potassium levels, such as spironolactone, triamterene, and amiloride.
- The NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)—aspirin, Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve), as well as celecoxib, diclofenac (also known as indomethacin), diclofe, and more;
- Insulin or diabetes medication.
- Medication to prevent organ transplant rejection, for example, stemsirolimus, sirolimus, temsirolimus, and everolimus, as well as.
- Blood pressure or heart medication.
This list isn't exhaustive. Other medications can affect benazepril, such as prescription and OTC medicines, vitamins, and herbal products.