Autoimmune diseases are conditions where the immune system attacks itself, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. Over 80 autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid, lupus, and multiple sclerosis, are known. Type 1 diabetes and psoriasis are also autoimmune conditions. These disorders can affect almost any part of the human body, and they can present with various symptoms. This makes them hard to diagnose and treat. Genetic and environmental factors may play a part in autoimmune disorders. The most common autoimmune diseases and their treatments are listed below:
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
The autoimmune disorder causes swelling and stiffness in the joints. This condition is caused by the immune system attacking the synovium lining the joints. It can cause inflammation and damage.
NSAIDs are anti-inflammatory medications that help reduce pain and inflammation.
DMARDs:
These drugs suppress the immune system to slow or stop the progress of RA.
Biologic agents are a class of DMARDs that target molecules within the immune system involved in inflammation.
Physical therapy can improve joint flexibility and function.
SLE:
SLE is an autoimmune disease that affects multiple body organs, including the kidneys, skin, and heart. When the immune system attacks healthy organs and tissues, inflammation and damage occur. SLE can be treated by:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). These drugs can reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and suppress your immune system.
Antimalarial medications:
These drugs can reduce flare-ups and help control symptoms.
Immunosuppressive drugs:
These drugs suppress the immune system and can reduce inflammation.
SLE can be treated with lifestyle changes, including avoiding sunlight and managing stress. These factors may trigger flare-ups.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS):
MS is a central nervous system disorder that causes symptoms like muscle weakness, numbness, and vision and coordination problems. The condition is caused by the immune system attacking the protective coating of nerve fibers around the brain and spine cord, called myelin. The following are possible treatment options for MS:
Drugs that slow the progression of MS can be found in disease-modifying therapies. These medications reduce the frequency and severity of relapses.
Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and help speed recovery after relapses.
Immunosuppressive Agents:
These drugs suppress the immune system, reducing the severity and frequency of relapses.
Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy are all possible treatments for MS. These therapies can improve mobility, strength, and communication.
Type I diabetes:
The pancreas is affected by this autoimmune disease, which leads to a lack of insulin production and high blood sugar levels. When the immune system attacks the cells that produce insulin in the pancreas, it can cause diabetes. Type 1 diabetes can be treated by:
Insulin therapy is required for people with type 1 diabetes who need insulin injections or insulin pumps to control their blood sugar levels.
Regular blood sugar monitoring can help those with type 1 diabetes manage their condition by adjusting insulin doses and making other lifestyle changes.
Lifestyle changes: Exercise and diet can help improve blood sugar control and overall health.
Another treatment for type 1 diabetes is pancreatic islet cell transplantation. This is an experimental procedure that involves transplanting insulin-producing cells into the pancreas.
Hashimoto thyroiditis:
This autoimmune disease affects the thyroid, causing symptoms such as fatigue and weight gain. It can also cause cold intolerance. When the immune system attacks thyroid glands, inflammation, and damage occur. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis can be treated by:
Thyroid hormone therapy:
Those with an underactive gland require thyroid hormone therapy. This involves taking synthetic thyroid hormones daily to regulate metabolism.
It is important to monitor thyroid hormone levels regularly and the symptoms of thyroid replacement therapy.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis can be treated with lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and a healthy diet. These can improve health and manage symptoms.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD):
IBD is a digestive disorder with Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss. These conditions can cause damage and inflammation to the lining of the digestive system. IBD can be treated by:
Anti-inflammatory drugs reduce inflammation of the digestive tract.
Immunosuppressive Agents:
Drugs such as methotrexate and azathioprine can suppress the immune system.
Biologic agents (such as infliximab or adalimumab) target specific molecules involved in inflammation and can reduce inflammation.
Other treatments may include dietary modifications, such as avoiding foods that trigger symptoms or surgery. This may sometimes be required to repair damaged tissue or remove it.
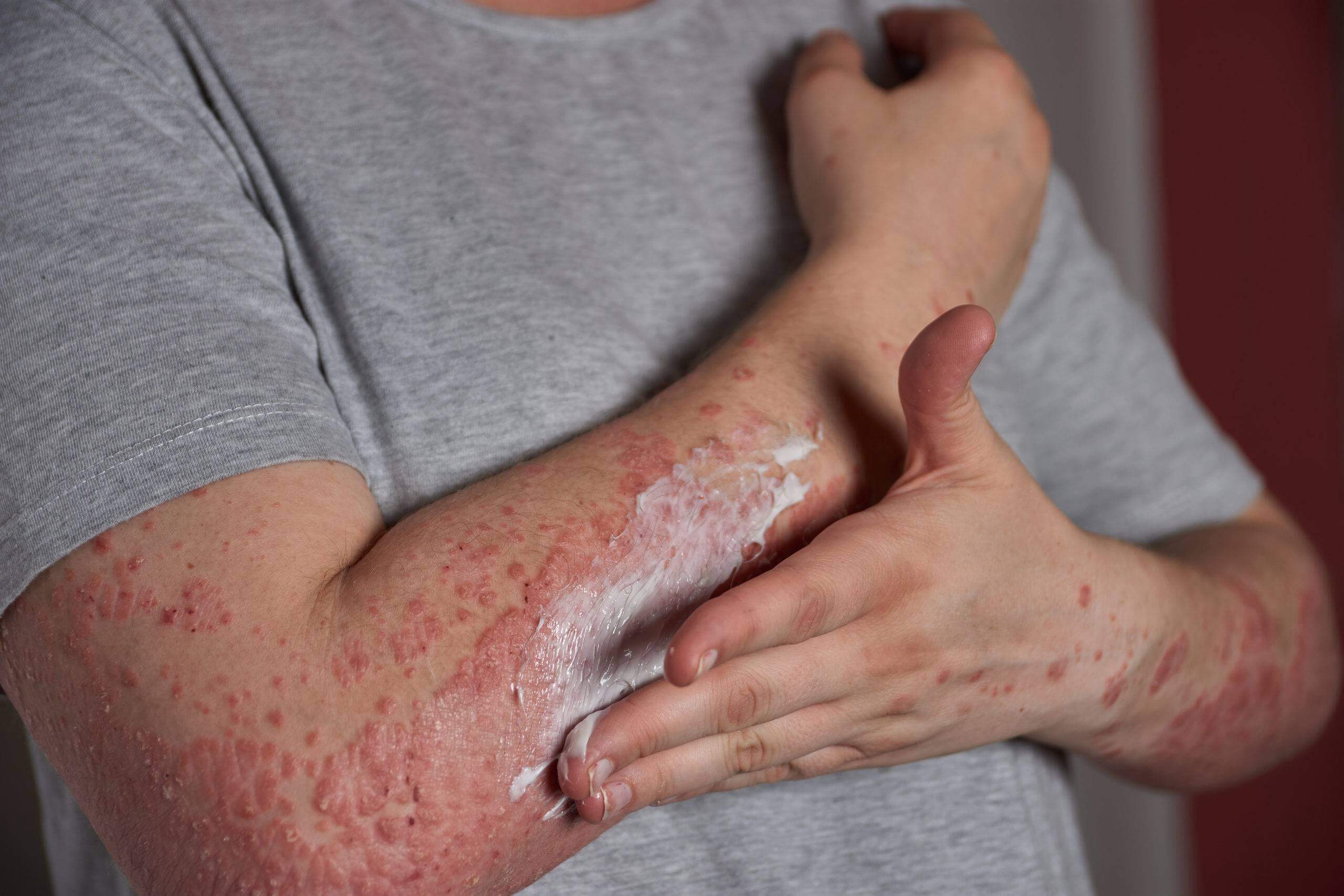
Psoriasis:
This autoimmune disease affects the skin and can cause red, scaly, itchy patches. Psoriasis is caused by the immune system triggering the overproduction and scaliness of skin cells.
Topical creams can reduce skin irritation and inflammation.
Phototherapy:
The treatment involves exposing skin to ultraviolet radiation to reduce inflammation and slow the growth of new skin cells.
Systemic medications can suppress the immune system, reduce inflammation, and include biological agents.
Treatments for psoriasis can include lifestyle changes such as stress management, avoiding triggers, and supportive care such as moisturizing skin and topical treatments that reduce itching.
Sjogren syndrome:
This autoimmune disease affects the glands that produce saliva and tears, causing a dry mouth and eyes. This condition is caused by the immune system attacking the glands, which produce tears and saliva. Sjogren’s Syndrome can be treated in several ways.
Artificial tears can help reduce irritation and dryness of the eyes.
Saliva substitutes can lubricate and soothe the mouth, reducing dryness and discomfort.
Immunosuppressive Agents:
These medications can suppress the immune system, reduce inflammation, and include corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and other similar drugs.
Sjogren’s Syndrome can be treated with lifestyle changes such as staying hydrated, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and dental care such as fluoride treatments.
Exercise, stress reduction, and a healthy eating plan can also help to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for people with autoimmune diseases. People with autoimmune diseases should work closely with their doctors to determine the best treatment. Even though autoimmune disorders are difficult to manage, people can still lead active and full lives with proper treatment.